There are many different sorting algorithms that can be used to arrange data in a specific order.
What is time complexity?
The time complexity of a sorting algorithm refers to the amount of time it takes to sort a list of a given size.
What is space complexity?
The space complexity refers to the amount of additional memory space that the algorithm requires to perform the sort.
Some common sorting algorithms with their respective time and space complexities:
Bubble sort:
How it works?
This algorithm compares adjacent elements and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. It repeats this process until the list is sorted.
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(1)
Selection sort:
How it works?
This algorithm selects the smallest element in the list and swaps it with the first element. It then selects the second smallest element and swaps it with the second element, and so on, until the list is sorted.
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(1)
Insertion sort:
How it works?
This algorithm starts with the second element in the list and compares it to the first element. If the second element is smaller, it is swapped with the first element. The algorithm then compares the third element to the first and second elements, and swaps it with the appropriate element. This process continues until the list is sorted.
Time complexity: O(n^2)
Space complexity: O(1)
Merge sort:
How it works?
This algorithm divides the list into two smaller lists, sorts each of these lists, and then merges the two sorted lists back together.
Time complexity: O(n*log(n))
Space complexity: O(n)
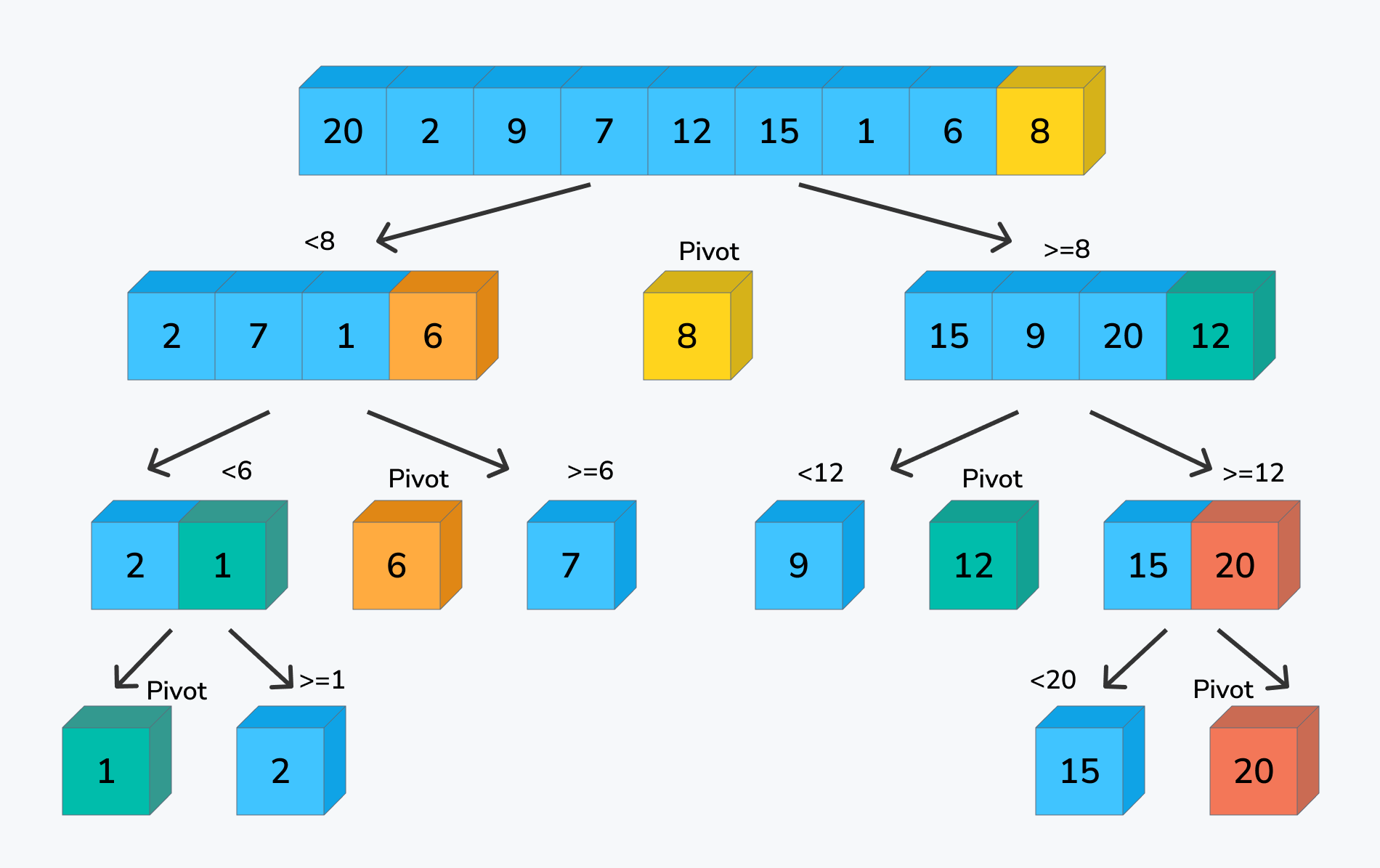
Quick sort:
How it works?
This algorithm selects a “pivot” element and rearranges the list so that all elements less than the pivot are placed before it and all elements greater than the pivot are placed after it. The algorithm then repeats this process on the sublists to the left and right of the pivot until the list is sorted.
Time complexity: O(n*log(n))
Space complexity: O(log(n))
Heap sort:
How it works?
This algorithm uses a data structure called a heap to sort the list. It first builds a heap from the list, and then repeatedly removes the largest element from the heap and adds it to the sorted list until the heap is empty.
Time complexity: O(n*log(n))
Space complexity: O(1)
Counting sort:
How it works?
This algorithm works by counting the number of occurrences of each unique element in the list and using this information to determine the position of each element in the sorted list.
Time complexity: O(n+k) where k is the number of unique elements in the list
Space complexity: O(k)
These are just a few examples of the many different sorting algorithms that are available. Each algorithm has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which algorithm to use will depend on the specific requirements of the problem at hand.
About complexity:
The time complexity of a sorting algorithm is typically expressed using big O notation, which gives an upper bound on the number of steps the algorithm takes to complete. For example, an algorithm with a time complexity of O(n^2) will take no more than a quadratic number of steps to sort a list of size n. The space complexity is typically expressed in terms of the size of the input list. It’s important to note that these time and space complexities are based on the worst-case scenarios for each algorithm. In practice, some algorithms may perform better than their worst-case complexities would suggest, depending on the specific input data.
